In the years after Timor-Leste regained independence from Indonesia, ‘oil fever’ took hold in the country – an intense contagious excitement about the prospect of oil wealth enabling a profound societal transformation and leading to full independence through resource sovereignty.
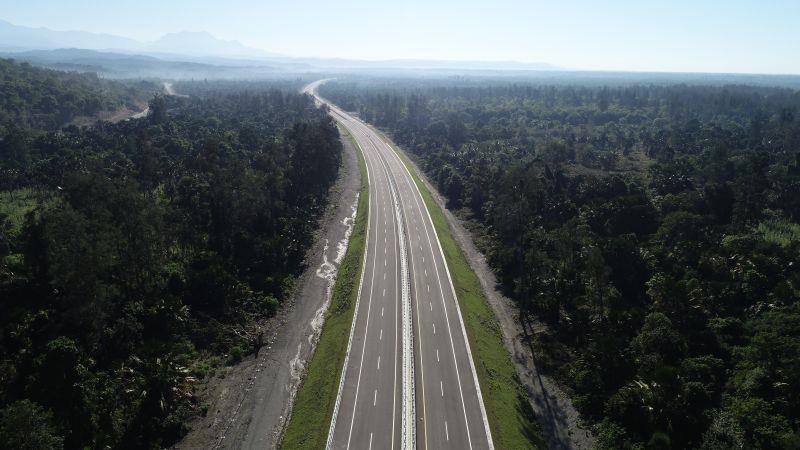
This is when the government of Timor-Leste launched a plan for the implementation of the Tasi Mane project, a large oil development project aimed at transforming the thinly populated south coast into a futuristic, high-modernist, state-planned oil and gas infrastructure by 2020.
Critics argued that the Tasi Mane project was economically and technically unviable and that it would have detrimental effects on local residents. So, to persuade affected communities to relinquish large stretches of land for the project, politicians and oil company employees mobilised customary practices traditionally associated with ritual authorities.
Their ability to regulate ‘nature’ came to be seen as a sign of their legitimacy to implement this mega project. By doing so, they combined practices based on two seemingly incompatibly logics: animism and extractivism.
This paper examines how these two seemingly opposed logics transformed each other in the making of the post-revolutionary state in Timor-Leste. The central argument is that animism and extractivism not only intersect as they were incorporated into modes of national governance, but that they were constituted in dialogical interaction.
Facebook event